Environmental Impact Reduction Activities
– Group Performance and New Targets –
FY2019 Targets and Performance
Theme❶ CO2 Emissions Reduction

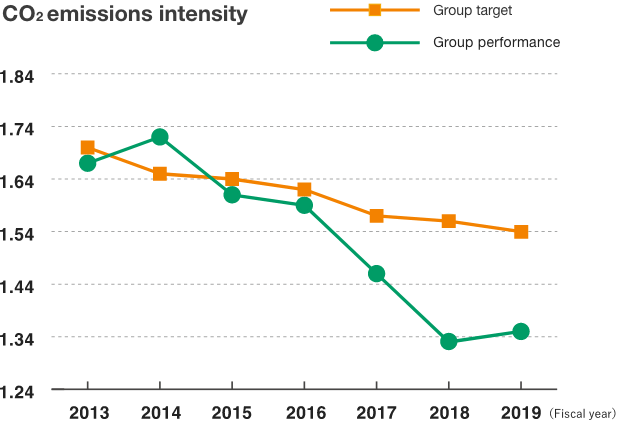
In accordance with the energy facility changeover implemented at the Fuji plant in FY2017, the raw fuel was switched from heavy oil to liquid natural gas (LNG). The effects of this change are starting.
*Release, usage and generation per production volume
■FY2020-2022 New Targets for the Next Mid-Term Business Plan
- Overall group
-
CO2 emissions intensity
21.5% reduction
(compared with FY2013)
- Mid-to-Long-Term Vision
- By FY2030, reduce
CO2 emissions intensity by 26% or more compared with FY2013
Theme❷ Energy Saving Activities


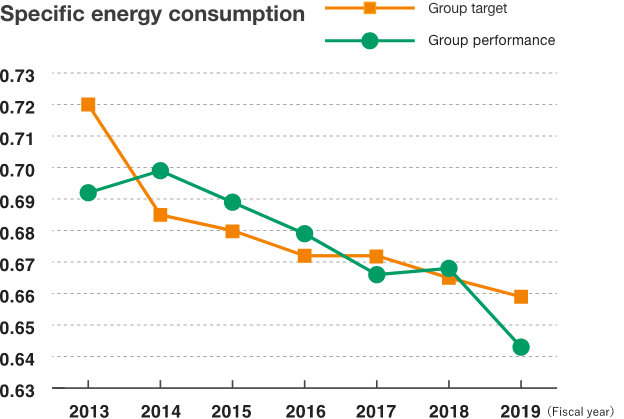
The effects of the changeover to energy-efficient boilers, as well as other changes made since FY2017, including replacement of mercury vapor lighting with LED lights inside plants and introduction of a steam compressor-driven flash steam reuse system, are starting.
■FY2020-2022 New Targets for the Next Mid-Term Business Plan
- Overall group
-
Specific energy consumption
1% or more per year reduction
(compared with FY2019)
Theme❸ Reducing Emissions of Chemical Substances (PRTR Substances*)

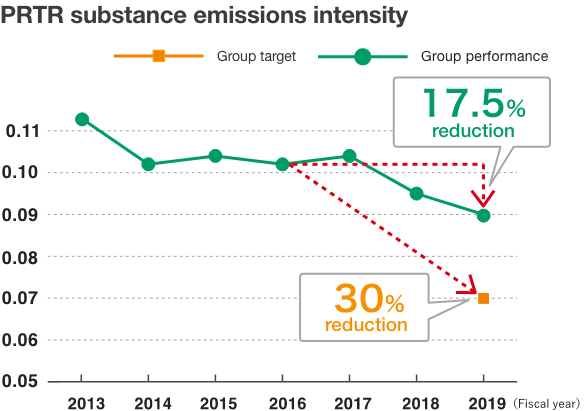
With regard to the calculation of PRTR substance emissions intensity, it was previously the practice to not revise past figures when new emission sources were identified. However, due to the fact that this approach makes it difficult to analyze the performance of Polyplastics’ environmental impact reduction activities. Therefore this graph was retroactively corrected based on revised figures through FY2015. As a result, PRTR substance emissions intensity for this fiscal year is 17.5% lower than it was for FY2016 (reference year). Although the target was not met, facility upgrades have been performed in order to reduce emissions of dioxolane, which was the primary cause of the failure to achieve our target, and the effects of these upgrades are starting.
*Abbreviation of “Pollutant Release and Transfer Register”
Target / Designated Chemical Substances
| 1 | Antimony and its compounds |
|---|---|
| 2 | Xylene |
| 3 | Silver and its water-soluble compounds |
| 4 | 1,4-dioxane |
| 5 | 1,3-dioxolane |
| 6 | Hydroterphenyl |
| 7 | Terephathalic acid |
| 8 | Dimethyl terephthalate |
|---|---|
| 9 | Triethylamine |
| 10 | 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene |
| 11 | N-butyl-2,3-epoxypropyl ether |
| 12 | Benzene |
| 13 | Formaldehyde |
| 14 | Molybdenum and its compounds |
■FY2020-2022 New Targets for the Next Mid-Term Business Plan
- Overall group
-
Establishment of VOC Measurement Methods
and Benchmarks
- Fuji plant
-
PRTR substance emissions
50% or more reduction
(compared with FY2019)
Theme❹ Industrial Waste Reduction


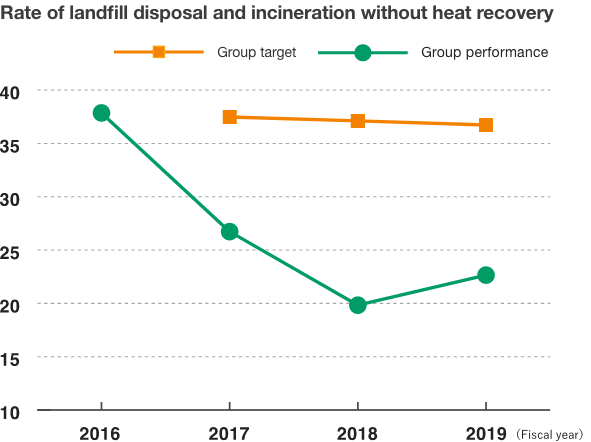
Previously, the target rate has been calculated based on the total for incineration without heat recovery, landfill disposal and recycling; however, in order to make it easier to determine the degree to which zero-emission targets (keeping the rate of landfill disposal and incineration without heat recovery to less than 1%), the calculation method and presentation of data has been revised.
For this fiscal year, the calculated rate was 40.2% lower than tha for FY2016.
■FY2020-2022 New Targets for the Next Mid-Term Business Plan
- Overall group
-
Rate of landfill disposal and incineration without heat recovery
Under 16%
- Mid-to-Long-Term Vision
- By FY2030, achieve and maintain
zero-emissions targets for the entire group
Activity Topics
Kaohsiung Plant (Taiwan)
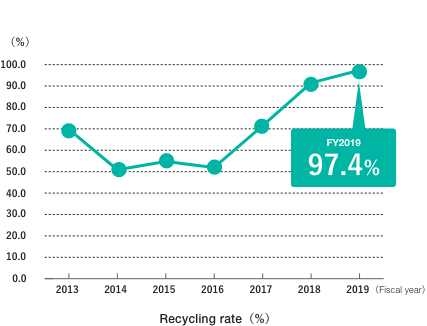
Achieves Waste Recycling Rate of 97.4%
Activity Details
The Kaohsiung plant has been undertaking zero-emission activities* on an ongoing basis since FY2013 and has achieved a waste recycling rate of 97.4% for this fiscal year. A major contributor to this success has been the significant reduction in the amount of sludge (highly noxious precipitate produced during the drainage water treatment process) the plant produces.
The sludge produced during drainage water treatment contains a great deal of moisture which significantly adds to its volume, and around 50 tons/month of sludge was being produced. In the past, this sludge would be disposed of in landfills, but in order to reduce environmental impact and improve the noxious odor problem that the sludge creates, equipment for performing drying treatment of the sludge was introduced into the plant. A point was also made to select environmentally-friendly equipment that utilizes an energy-efficient heat pump producing very little CO2. Through drying treatment, the volume of sludge was reduced, enabling the plant to get down to its target of 20 tons/month while also resolving the noxious odor problem.
*Activities aimed at keeping the percentage of waste disposed of via landfill disposal and incineration without heat recovery, both of which have a significantly negative impact on the environment, to less than 1%
-

Kaohsiung plant
-

Sludge drying treatment equipment
-
■Change in sludge as a result of drying treatment
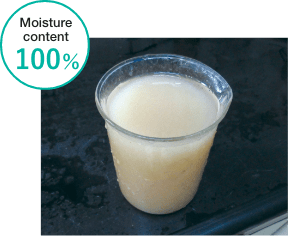


Volume reduced and odor problem solved

Wastewater treatment equipment
Kaohsiung Plant (Taiwan)
Reducing industrial wastewater by 36,000 tons/year through advanced wastewater treatment
This fiscal year, the Kaohsiung plant has introduced advanced wastewater treatment equipment that will help reduce the amount of industrial wastewater it produces. This equipment is highly efficient at removing suspended solids (particulate material with a diameter of 2 mm or less) and has reduced industrial wastewater by 3,000 tons/month. In addition, the water treated by this equipment can be recycled for use as cleaning water during the manufacturing process, thereby reducing water usage by 3,600 tons/month.

Leuna Plant
Leuna Plant (Germany)
Reduce CO2 emissions by 365 tons annually by changing cooling equipment and processes
In FY2019, Leuna plant undertook optimization of its cooling equipment and processes used in the production of pHBA, which is a key raw material of LCP resin. As a result of introducing fouling-tolerant heat exchangers and improved manufacturing methods, the 10℃ cooling water which normally required electrical power to produce could be replaced with normal cooling water, thereby reducing CO2 emissions by roughly 365 tons per year. This initiative qualified for the government’s energy conservation support program for companies and, as a result, received a subsidy of €1,500 from the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany.








